Lake Taupo
| Lake Taupo | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Location | Taupo District, Waikato Region, North Island |
| Lake type | crater lake, oligotrophic |
| Primary inflows | Waitahanui River, Tongariro River, Tauranga-Taupo River |
| Primary outflows | Waikato River |
| Catchment area | 3,487 km2 (1,346 sq mi) |
| Basin countries | New Zealand |
| Max. length | 46 km (29 mi) |
| Max. width | 33 km (21 mi) |
| Surface area | 616 km2 (238 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 110 m (360 ft) |
| Max. depth | 186 m (610 ft) |
| Water volume | 59 km3 (14 cu mi) |
| Residence time | 10.5 years |
| Shore length1 | 193 km (120 mi) |
| Surface elevation | 356 m (1,168 ft) |
| Islands | Motutaiko Island (11 ha)[1][2] |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
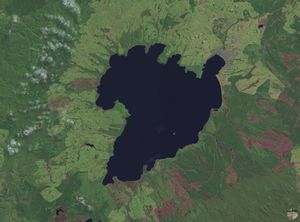
Lake Taupo is a lake situated in the North Island of New Zealand. With a surface area of 616 square kilometres (238 sq mi), it is the largest lake by surface area in New Zealand, and the largest freshwater lake by surface area in Oceania.
Lake Taupo has a perimeter of approximately 193 kilometres, a deepest point of 186 metres. It is drained by the Waikato River (New Zealand's longest river), while its main tributaries are the Waitahanui River, the Tongariro River, and the Tauranga Taupo River. It is a noted trout fishery with stocks of introduced brown trout and rainbow trout.
Contents |
Lake formation and volcanism
Lake Taupo lies in a caldera created by a supervolcanic eruption which occurred approximately 26,500 years ago. According to geological records, the volcano has erupted 28 times in the last 27,000 years. It has ejected mostly rhyolitic lava, although Mount Tauhara formed from dacitic lava.
The largest eruption, known as the Oruanui eruption, ejected an estimated 1,170 cubic kilometres of material and caused several hundred square kilometres of surrounding land to collapse and form the caldera. The caldera later filled with water, eventually overflowing to cause a huge outwash flood.[3]
Several later eruptions occurred over the millennia before the most recent major eruption, which occurred in 180 CE. Known as the Hatepe eruption, it is believed to have ejected 100 cubic kilometres of material, of which 30 cubic kilometres was ejected in the space of a few minutes. This was one of the most violent eruptions in the last 5,000 years (alongside the Tianchi eruption of Baekdu at around 1000 and the 1815 eruption of Tambora), with a Volcanic Explosivity Index rating of 7. The eruption column was twice as high as the eruption column from Mount St. Helens in 1980, and the ash turned the sky red over Rome and China. The eruption devastated much of the North Island and further expanded the lake. The area was uninhabited by humans at the time of the eruption, since New Zealand was not settled by the Māori until several centuries later at the earliest. Taupo's last known eruption occurred around 210 CE, with lava dome extrusion forming the Horomatangi Reefs, but that eruption was much smaller than the 180 CE eruption.
The 180 eruption was one of the largest in recorded history. The skies and sunsets formed from this eruption were noted by Roman and Chinese observers. Any possible climatic effects of the eruption would have been concentrated on the southern hemisphere due to the southerly position of Lake Taupo.[4]
Underwater hydrothermal activity continues near the Horomatangi vent,[5] and the volcano is currently considered to be dormant rather than extinct.
Biota
Much of the watershed of Lake Taupo is a beech and podocarp forest with associate understory ferns being Blechnum filiforme, Asplenium flaccidum, Doodia media, Hymenophyllum demissum, Microsorum pustulatum and Microsorum scandens, and some prominent associate shrubs being Olearia ranii nd Alseuosmia quercifolia.[6]
Native faunal species in the lake include northern koura or crayfish (Paranephrops planifrons) and kokopu or whitebait (Galaxias species). The lake is noted for stocks of brown trout (Salmo trutta) and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss), introduced from Europe and California respectively in the late nineteenth century. There has also been a subsequent introduction of smelt (Retropinnidae species) as a food for the trout.
A community of sponges and associated invertebrates live around the underwater geothermal vents.[5]
Tourism

Tourism is a major component of Taupo's commercial sector, and the city attracts over 1.2 million visitors per year. The busiest time for the industry is the high summer season around Christmas and New Year.
The lake area has a temperate climate. Maximum temperatures range from 24°C in January to 15°C in July, while the night temperatures range from 16°C in summer down to 5°C in winter. Most rain falls in summer.[7]
Taupo hosts the Lake Taupo Cycle Challenge, a cycling tour around the lake which can take anywhere between four and ten hours. Hundreds of volunteers from the Taupo township are involved in the event. Skydiving is a popular local sport and tourist attraction.
Gallery

See also
- List of volcanoes in New Zealand
- Taupo Volcanic Zone
References
- ↑ Motutaiko Island, Department of Conservation.
- ↑ Laurence Cussen (1887). Lake Taupo, pp 328–331 in Notes on the Physiography and Geology of the King Country, Transactions of the Royal Society of New Zealand, 20, 317–332.
- ↑ Manville, Vern & Wilson, Colin J. N. (2004). "The 26.5 ka Oruanui eruption, New Zealand: a review of the roles of volcanism and climate in the post-eruptive sedimentary response". New Zealand Journal of Geology & Geophysics 47: 525–547. http://www.rsnz.org/publish/nzjgg/2004/042.php.
- ↑ Climate, History and the Modern World, Lamb,H. (1995), Routledge
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 C. E. J. de Ronde, P. Stoffers, D. Garbe-Schönberg, B. W. Christenson, B. Jones, R. Manconi, P. R. L. Browne, K. Hissmann, R. Botz, B. W. Davy, M. Schmitt and C. N. Battershill (2002). "Discovery of active hydrothermal venting in Lake Taupo, New Zealand". Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 115: 257–275. doi:10.1016/S0377-0273(01)00332-8.
- ↑ C. Michael Hogan. 2009. Crown Fern: Blechnum discolor, Globaltwitcher.com, ed. N. Stromberg
- ↑ GHCN Climate Database, Goddard Institute of Space Studies, www.giss.nasa.gov
- Ben G. Mason; David M. Pyle, and Clive Oppenheimer (2004). "The size and frequency of the largest explosive eruptions on Earth". Bulletin of Volcanology 66 (8): 735–748. doi:10.1007/s00445-004-0355-9.
- "Taupo". Global Volcanism Program, Smithsonian Institution. http://www.volcano.si.edu/world/volcano.cfm?vnum=0401-07=. Retrieved 2009-01-01.